The development of water electrolysis for hydrogen production can be divided into three historical stages: the nascent stage, initiation stage, and rapid development stage. As the path toward carbon neutrality accelerates, water electrolysis for hydrogen production has come into the public spotlight. The development of electrolyzers, a key component of this process, spans several significant periods.
Nascent Stage (1800–1939):
In 1800, Nicholson and Carlisle first extracted hydrogen and oxygen using electrolysis.
In 1888, Russian scientist Lachinov patented the first unipolar electrolyzer.
By 1900, Schmidt had invented the first industrial electrolyzer.
In 1924, Noeggenrath patented a pressurized electrolyzer capable of reaching 100 bar.
In 1927, the world’s first large-scale filter-press electrolyzer was installed in Notodden, Norway, by Norsk Hydro, with a hydrogen production capacity of 10,000 m³/h.
By 1939, Canada installed the first large-scale box-type electrolyzer with a capacity of 17,000 m³/h.
Initiation Stage (1940–2014):
In 1948, the first high-pressure industrial electrolyzer was developed.
During the 1950s and 1960s, China introduced technology from the Soviet Union as part of its assistance projects, laying the groundwork for domestic innovation.
By the 1990s, China achieved the localization of electrolyzers and began exporting complete systems.
In 2014, the EU proposed a development roadmap for PEM (Proton Exchange Membrane) water electrolysis technology.
Rapid Development Stage (2015–Present):
Significant advancements in water electrolysis technology and industrial scale-ups occurred globally.
In 2015, Siemens and Linde Group built the world's first MW-scale wind-powered PEM water electrolysis demonstration project in Germany.
In 2019, Shell and ITM Power developed a 10 MW PEM electrolysis hydrogen plant at the Rheinland Refinery in Germany, producing 1,300 tons of green hydrogen annually.
Through decades of technological breakthroughs, both globally and in China, water electrolysis for hydrogen production has achieved commercial viability. With the installation capacity of electrolyzers reaching the gigawatt (GW) scale, PEM technology has become increasingly mature, driving the growth of the hydrogen industry in clean energy applications.
PEM Membrane for Electrolyzer
As this field continues to develop rapidly, one of the critical components driving the efficiency and effectiveness of water electrolysis for hydrogen production is the Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) used in PEM electrolyzers. Our PEM membrane plays a vital role in ensuring the efficient production of hydrogen by enabling high conductivity and superior performance in harsh electrochemical environments.
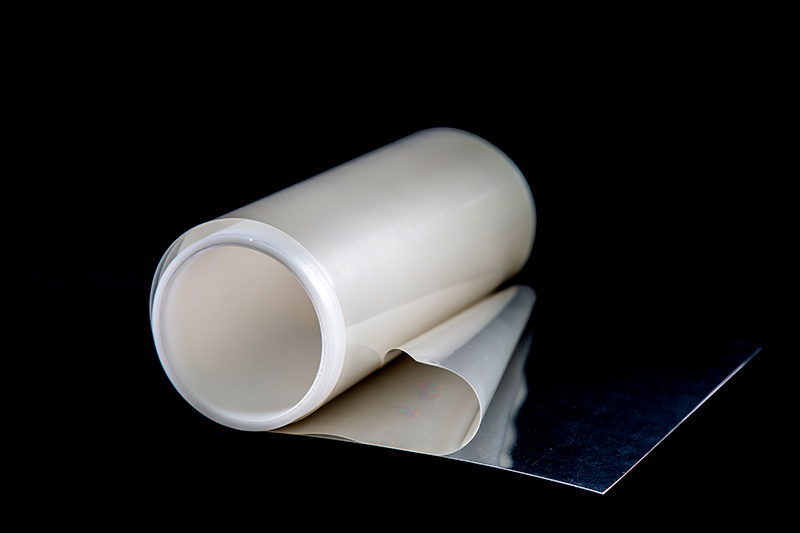

With the increasing demand for clean hydrogen production, our PEM membrane is designed to meet the needs of the latest electrolyzer technologies, offering high durability, low energy consumption, and reliability. Whether in large-scale commercial hydrogen production or smaller, specialized systems, our PEM membranes are the ideal choice for companies looking to enhance their electrolysis processes.